
Kiyomi Sakata
Iwate Medical University, Japan
Title: Preventive effect of Lactococcus lactis subsp.lactis JCM 5805 yogurt intake on influenza infection among school children
Biography
Biography: Kiyomi Sakata
Abstract
Objective: A community-based intervention study was conducted to examine the effect of consumption of JCM 5805 yogurt on influenza incidence rates and the cumulative incidence rates among schoolchildren in Iwate Prefecture, Japan.
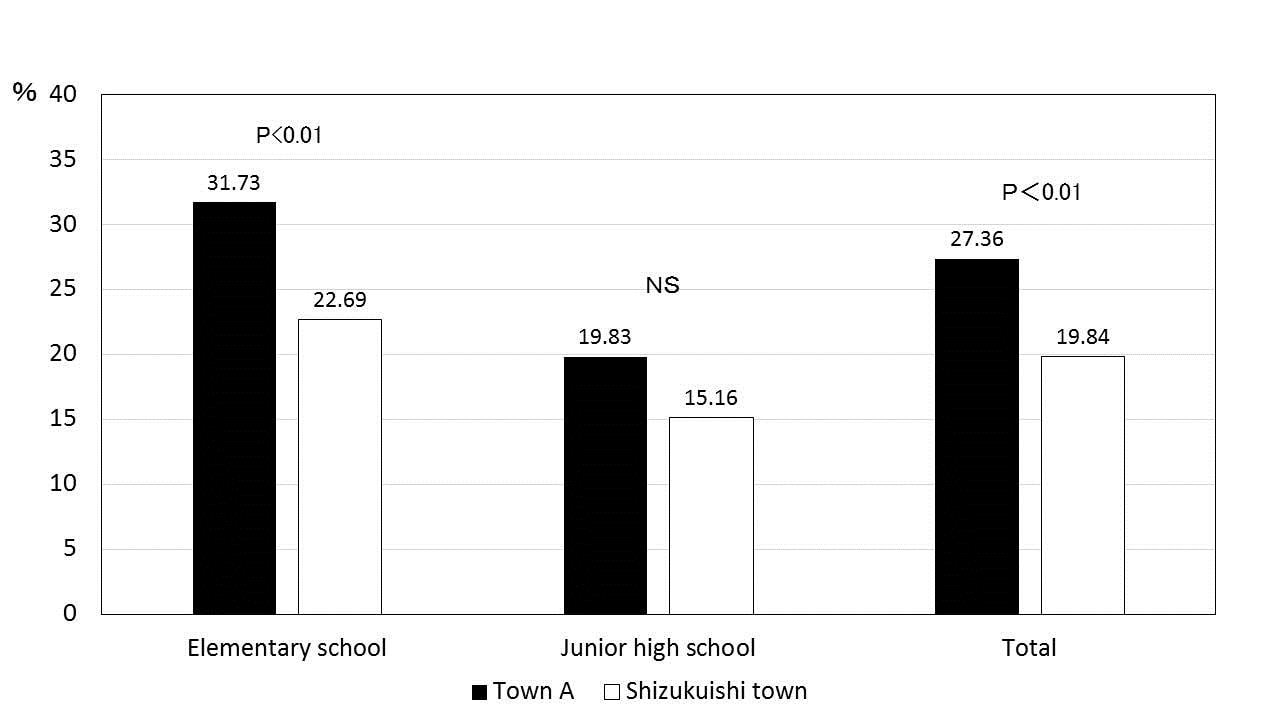
Methods: Schoolchildren and their parents in Shizukuishi town were told of the purpose, frequency and duration of JCM 5805 yogurt administration. The number of elementary schoolchildren in Shizukuishi town was 780 while that of junior high school students in Shizukuishi town numbered 475. The number of elementary schoolchildren in neigh-boring town A was 208 and that of junior high school students in town A was 121. JCM 5805 yogurt was delivered three times a week to all elementary schools and junior high schools in Shizukuishi town from January 16 through March 18, 2015. The incidence rate was calculated every week as the maximum case number divided by the number of schoolchildren in each school. The cumulative incidence rate was calculated as the total case number during the period when JCM 5805 yogurt was delivered divided by the number of schoolchildren in each school.
Results: JCM 5805 yogurt intake was associated with a two-thirds reduction in influenza incidence rates in Shizukuishi town schoolchildren compared with those of town A. Furthermore, the cumulative incidence rates of the elementary school and combined data from the elementary school and junior high school were significantly lower than those of neighbor town A.
Conclusion: JCM 5805 yogurt intake reduced both the incidence rates and cumulative incidence rates of influenza.
Recent Publications:
- Koeda Y, Tanaka F, Segawa T, et al. (2016) Comparison between urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio and urine protein dipstick testing for prevalence and ability to predict the risk for chronic kidney disease in the general population (Iwate-KENCO study): a prospective community-based cohort study. BMC Nephrology. 17(46):1-8.
- Sato T, Kishi M, Suda M, et al. (2017) Prevalence of Candida albicans and non-albicans on the tongue dorsa of elderly people living in a post-disaster area:a cross-sectional survey. BMC Oral Health. 17(51):1-10.
- Satoh A, Arima H, Ohkubo T, et al. (2017) Associations of socioeconomic status with prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in a general Japanese population: NIPPONDATA2010. J Hypertens. 35(2):401-408.

